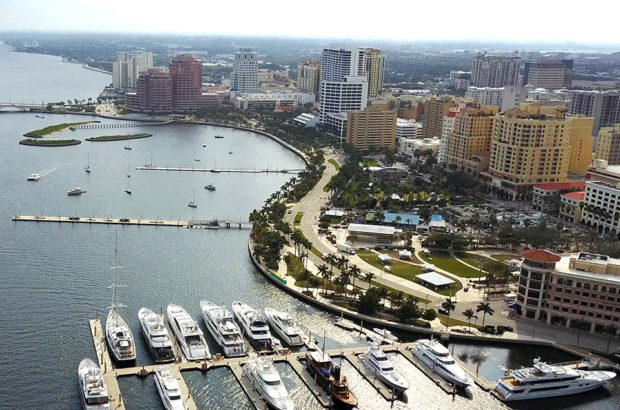
During the last year we have been busy with several projects and competitions (including the latest Open Shore project for West Palm Beach) which didn’t give us the time to look back and reflect on some of our projects from the last few years.
As maybe some of our readers know, Ecosistema Urbano has been working on several large-scale projects in Latin America since August 2014 when we won a competition to develop the Master Plan of the Historical Center of Asuncion, Paraguay. In 2015, we accomplished another significant project: the participatory process Centro Histórico Abierto for the transformation of the historical center of Distrito Central, capital of Honduras. We also worked on the transformative Cuenca RED project which acted on the Public Space Reactivation Plan of the Historical Center of Cuenca, Ecuador. After the first experience in Paraguay, we had another project in the city of Encarnación, giving origin to the Plan Encarnación Más, composed by an Urban and Territorial Planning and Sustainability Plan.
In these four cases, the urban issues and the peculiar situations that required our intervention were distinct yet shared many common features. More specifically, the enthusiasm and interest shown by the people directly and indirectly involved was apparent throughout all of the projects, but also the opportunities that these experiences have given us as an architecture firm, to test ideas, tools, and methodologies.
CONTEXT
Although they share the same area of origin, each of these cities has developed unique problems and issues. Some of these, such as the ones found in Encarnación, are physical-territorial matters such as the recent loss of the city center because of the controlled rise of the water level in the Yacyretá dam. That event led to the envisioning of a “Sustainable Development Plan” and “Urban and Territorial Ordering Plan” in order to prepare the city for the future. In the case of Cuenca, the need for a new plan was determined by a series of big changes underway: the definition of a new model of mobility and the progressive emptying of population that afflicts the historical center, World Heritage Site since 1999, and headquarters of most of the commercial, touristic and economic city’s activities. In the case of Asunción and of the capital of Honduras, the project regards the transformation and the regeneration (both physical and social) of their historic centers. The Distrito Central is part of the development framework of the new urban axis “Choluteca River”.

SOCIAL
1 – Participation
The first of the projects’ common keys are connected with the theme of sociability, expressed in the form of participation. The citizens’ involvement, promoted both through a series of organized activities and through online platforms, has been one of the cornerstones of our work in Latin America. We involve citizens because we believe that the citizen is the only force able to achieve a deep and lasting change in the urban environment and so they should not be just a passive receptor of the changes promoted by the city’s institutions. That’s why in some cases, as in that of Asunción with the ASU-LAB, a space was created which could serve as an interface between citizens and institutions: a place for the execution of the city planning but also an open place where each person or group can drive a new regeneration initiative or attend a course.


Organized activities with the citizens
Participatory activities, such as workshops and events, have been geared to address representative members of the city such as children, university students, “active agents”, citizens and institutions. For each of these categories we have developed, project after project, a series of ad hoc initiatives.


Participatory process in Asunción, Encarnación, Cuenca and in Distrito Central
For the children we created a “toolkit” with which we had them reflect on their perception of the city and with which they could propose their ideal vision for the city. The kit consists of portions of the city map on which they could draw and that, once recomposed, could recreate the overall image.

2 – Urban actions
These activities were followed by a series of urban actions so that the results could be shown tangibly in the city. In the case of Distrito Central, ideas were gathered in a week of workshops with 80 students from the three major universities in the city and have been translated into urban actions like “Las Gradas de la Leona“. The staircases are indispensable spaces in a city with a very distinct topography as Tegucigualpa. But in the city these vertical connections are often perceived as inhospitable, dangerous, and dirty places and therefore they are cut off from any kind of activity. The students’ work was aimed at legitimizing these stairs as a public space through cleanliness, decor, lighting, and the organization of a series of activities that achieved resounding success and participation.

Socialization along “Las gradas de la Leona”
In the case of Encarnación, one of the proposals that has distinguished our approach in this project was the inclusion of a series of pilot projects that accompany and translate into concrete proposals within the “Plan de Desarrollo Sustentable” and the “Plan de Ordenamiento”. Among these, one of the most successful pilot projects was the “Proyecto Piloto Bicisienda“, whose purpose is to improve the quality of life of the inhabitants by optimizing the use of alternative mobility and by raising awareness of the value of sports and recreation. Again we have sought the cooperation of citizens by promoting a series of initiatives (such as the construction of bike lanes in the city) in which the citizens could feel protagonistic.

Proyecto Piloto Bicisienda
3 – Informative events
The disclosure of the participatory process to the citizenship, promoted both online through the project’s platforms and through open exhibitions, is a recurring phase in all four projects. We felt it important and necessary that each phase of the process was documented and could be easily accessible to all so that the citizens could be informed about the progress made in the project. Among these, the most scenic event, realized in Tegucigualpa, Cuenca and Encarnación, was the creation of a ” mosaico ciudadano“, a wall made of post-it notes with written words, phrases, and ideas about the city.

City mosaic in the several projects
SUSTAINABILITY
Another theme of our projects in Latin America is sustainable development expressed in various forms: care and attention to the environment, the introduction of an alternative mobility system, the importance of education to the environment as an engine of sustainability, and the development of the project made in collaboration between private initiatives and institutional management. In the case of Cuenca, for example, our intervention was partly required as a consequence of the municipality’s willingness to define a new model of mobility for the historical center of the city consisting of ceasing car traffic in the center and building a new tramway system. This new model of mobility has direct implications for the current urban dynamics, as well as on the public space, as it tries to reduce the vehicular load of the city, giving priority to pedestrians and cyclists. This, and the creation of quality public space, led to strengthen the social, economic, and cultural role of the city’s historical center making it more pleasant for residents and locals. Our aim is to activate a historical center that promotes social, economic, and environmental development, as well as a more livable, habitable, and inhabited historical center.
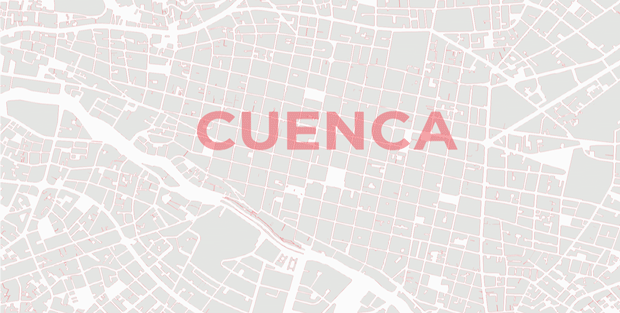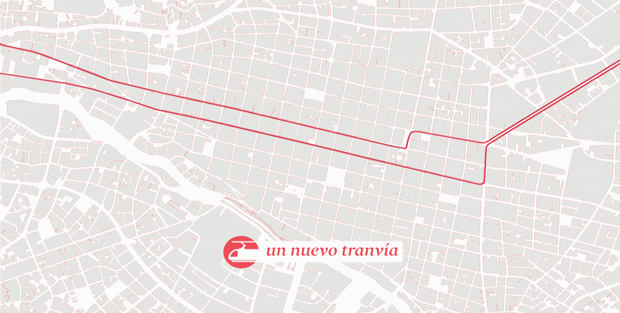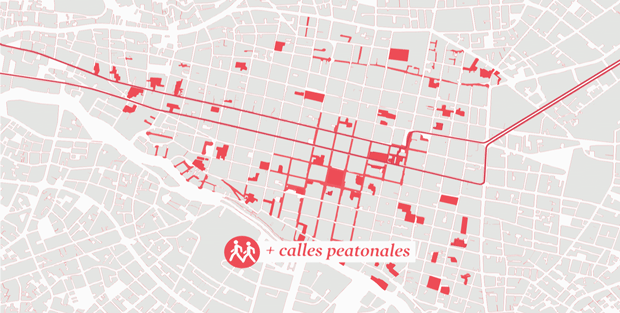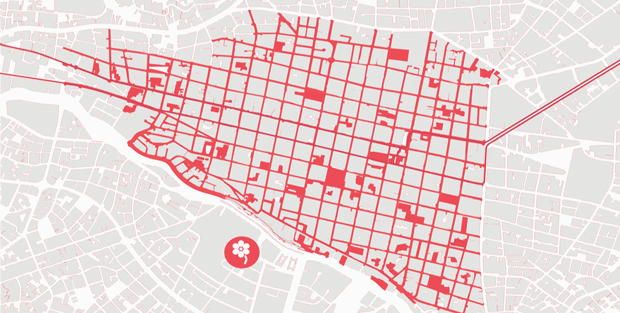
Cuenca’s plan is divided into four aspects: an urban acupuncture strategy, which proposes small / medium-scale interventions to recover areas with potential; a development of a network of active courtyards, by transforming the typical patios of Cuenca in catalysts capable of generating new synergies, connections, and interactions between residents, visitors and inhabitants; a guide to the historic center re-design, which defines the main lines for the design of the public space; a process of socialization, to define the “acopuntura” and the active patios network strategies. The intervention strategy in the square “Mary Corilè” in conjunction with the creation of “La casa en el árbol” is part of the active patios network strategy. This square is an unused and degraded space, perceived by the residents as an unpleasant and dangerous place.

The square “Mary Corilè”
Among the several interventions proposed, such as the re-furnishing of the square, traffic closure, and the design of activities in collaboration with the municipality, there’s also the creation of “La casa en el árbol“, a space included in the existing trees of the square where educational activities in relation to the theme of the environment can be carried out. “La casa en el árbol” is set up as a space to get in contact and be familiar with the nature, built in harmony with the surroundings. Inside there are several “environmental” classrooms in which one can study natural resources such as sun, wind, and water. More specifically, one can study: a system of photovoltaic panels that generate the energy needed for the lights, rainwater harvesting structures, and urban gardens as environmental and ecological experiences for schools and kindergartens. It is, ultimately, an open classroom in which a new form of pedagogy built on the respect for the environment is proposed, in order to increase awareness of the natural resources and of their use, as well as increase awareness of existing technologies.

In the case of Asunción we proposed a strategic plan with ten actions in order to promote a connection between the several parts of the city through the development of spaces, named “corridors“, and of individual buildings, named “urban catalysts“, which might act as drivers of change and benchmarks within the city. The corridors are divided into three types: those “green“, which introduce a new green infrastructure in specific parts of the existing roads; those “civic“, which consist of a new network of public spaces along the roads in order to connect the most important historic and government buildings; those “dynamic“, aimed at creating active urban environments and encourage economic and cultural activities.

Configuration of a charateristic dynamic corridor
Among the actions of Asunción strategic masterplan one concerns the economic and landscaping regeneration of the “Green Active Coast”. Due to its topography, this area is subject to cyclical floods because of the rising water level of the Paraguay River. That forces the inhabitants of the informal settlements who live there to move temporally. While fully respecting the identity of the river and of the existing topography, we have proposed the creation of a green lung with a large sports area in continuity with the Bicentennial Park. We also promoted the integration of the informal settlements both within the urban fabric and in the areas of new urban expansion.

The Encarnación masterplan incorporates within its own name the concept of “sustainability”, since it is composed of the “Plan of Sustainable Development” and of the “Plan of Urban and Territorial Organization”. The “Plan of Sustainable Development” will establish the standards and mechanisms for the growth and for the future development of the city according to the criteria of sustainability. The “Plan of Urban and Territorial Organization” aims at directing the use and the occupation of the territory in the urban and rural areas of the municipality. Officially, the city will face in the next twenty-four years an increase of the population amounted to 62,000 people, for whom it will be necessary to provide a massive increase in housing. The model we proposed to face this need refers to the sustainable principle of “the compact city.” Through the identification of a physical border for the city’s urban growth, we have protected the rural areas from new settlements. Moreover, we encouraged, through private and municipal initiatives, the densification of areas already developed, by filling the vacant urban lots and expanding pre-existing single-family homes.

Example of urban densification
The new interventions follow the principles of the bioclimatic architecture: large overhanging roofs and vegetation as protections from the hot summer sunlight, the use of wind to moderate the hot and humid climate of Encarnación, the reuse of rainwater, and the increase of the vegetation to absorb CO2 emissions.

TECHNOLOGY
In all four projects, technology represented an important collaborative tool to promote our work and to enable everyone to be constantly updated on ongoing progress, but also as a support for the participatory process, so that the involvement of the citizens would not be exhausted with the end of the activities organized, but could continue to map needs, issues, concerns and initiatives for those interested.
For this reason we have developed a platform, called Local-in (formerly What if ..?), which has been adapted to each project according to their personality and to the peculiarities of each participatory process, while maintaining a common format. Local-in is a free and accessible to everyone application of collective mapping. In it, registered users can add messages, photos and geolocalised links, sorting them into categories and labels. It’s easily installable and customizable, in perfect harmony with the spirit of the projects themselves, and it can be found for each project under the name “AsuMAP” for Asunción, with the name “Encarnación Más” for Encarnación, as “Cuenca RED” for Cuenca and with the name “Centro Histórico Abierto” for Distrito Central.